2008v17n2

Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
Pathophysiology & Treatment
A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & PHYSICIANS
By Russell Rothenberg, M.D.
Fibromyalgia remains an enigma to many
term "fibrositis" in 1904. In 1978, Drs. Smythe and
physicians despite its high prevalence in the U.S.
Moldofsky published the first scientific research on
population. Why do people chronically hurt all over,
the associated sleep pathology and the peripheral and
feel fatigued, and wake up feeling non-rested despite
central nervous system (CNS) pain sensitization that
getting 6-8 hours of sleep? Why do these symptoms
are important parts of the pathophysiology of FM.1 It
often appear to coexist with painful bowel, bladder,
was renamed fibromyalgia syndrome in 1990 with the
and jaw (TMJ) symptoms, as well as symptoms of
publication of official diagnostic criteria by the ACR.2
anxiety and cognitive impairment? The term
Only recently have we learned that FM is pre-
fibromyalgia (FM) was defined in 1990 by the
dominately caused by abnormalities in CNS pain
American College of Rheumatology (ACR). Since
sensitization and abnormal levels of neurotransmitters
then, the National Institutes of Health and other
and pain processing in the pain centers of the brain
institutions have dramatically increased their funding
and spinal cord.
for FM research, and there have been significant
FM is a relatively common illness estimated to
increases in published articles on fibromyalgia and
affect 4-10 million Americans. Demographic studies
medical conferences that include FM research and
show that it has a prevalence in the U.S. of 3 ½ % of
treatment in the curriculum.
all women and ½ % of all men over the age of 18
The major purpose of this article is to provide
years. These figures are similar to the prevalence of
information that patients can take to their doctors to
FM in other countries. It has been estimated that
help them make an accurate diagnosis of fibromyalgia
10-20% of patients in a rheumatologist's practice have
earlier and provide more effective treatment. With the
FDA-approved drugs for FM as well as other
There is a strong association between fibro-
treatments shown to be effective for FM in scientific
myalgia and many of the diseases rheumatologists
studies, doctors can help most FM patients. This
treat (rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, Sjögren's
article can also be used to provide objective scientific
syndrome, and systemic lupus) as well as certain
evidence for doctors who still are uncertain whether
infections (hepatitis C and Lyme disease). There is
fibromyalgia is a real medical entity. I've treated over
also a primary form of FM which appears to have
8,000 patients with FM and hope my experience can
a genetic basis that can affect multiple members of
help patients and doctors. Since my first article on
certain families.
this subject published in 2007 in Fibromyalgia
Despite all of the recent advances in the
Frontiers, there have been significant advances in
understanding of FM, the problem many patients still
research and treatment.
experience is a long delay between the onset of their
Fibromyalgia is not a new medical problem, it is
symptoms and their diagnosis of FM. Since patients
just better understood. It used to be called different
often have multiple symptoms, and there are no
names: "neurasthenia" and "muscular rheumatism"
objective lab tests or imaging studies that are
from the mid-1800's until Dr. Gowers created the
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
commercially available to make the diagnosis, they
anatomically specific tender points (See Figure 1) and
often face years of multiple medical evaluations,
requires the history of widespread pain being present
multiple specialists, a lot of frustration and suffering,
for at least three months. These tender points can be
and no answers. It would benefit the FM patient if
assessed by pressing on specific locations of the body
more primary care doctors considered fibromyalgia
with a pressure of 4 kg/m2 (enough pressure to blanch
in their differential diagnosis when a patient presents
the skin under the thumb nail). Pressing on these painful
with chronic pain and fatigue.
points can cause a very painful response, and the
FM is not an easy diagnosis to make. A careful
doctor should press gently initially and stop when it
history and complete physical examination are
hurts. The tender point exam is a good diagnostic test
necessary to make the diagnosis. It is essential for a
(88.4% sensitive and 81.1% specific to FM),5 but
doctor to do an adequate medical evaluation to "rule
tender points are not the only tender areas FM patients
out" other diseases that can mimic FM such as
have. They also have generalized increased pain to
hypothyroidism and rheumatic disease. There are also
normal touch all over the body (allodynia). It is very
numerous co-morbid conditions that can be the first
upsetting not to want to be touched or hugged by your
symptoms to appear in FM patients including irritable
loved ones, but that is what FM patients experience.
bowel syndrome, interstitial cystitis, vulvodynia,
Research doctors have shown in studies that the
temporomandibular joint syndrome, chronic fatigue
tender point exam is reproducible in FM patients. Dr.
syndrome, hyper-extensible joints/Ehlers Danlos
Bradley has demonstrated that lower pain threshold
Syndrome, non-restorative sleep disturbances, and
responses to thermal stimuli consistently are present
neurally mediated hypotension. When the diagnosis
in FM patients compared to normal controls, and this
of a patient with chronic musculoskeletal pain and
scientific finding has been reproduced by Dr. Geisser.6
fatigue is unclear, rheumatologists are available for
Drs. Gracely and Clauw have demonstrated with
functional brain MRI's that a FM patient's responseto painful stimuli consistently activates the areas of the
Scientific Findings That Support
brain associated with pain recognition at lower pain
Fibromyalgia As A Medical Entity
thresholds than in normal controls.7
Tender Point Exam & Pain Threshold Studies
The ACR definition of fibromyalgia includes the
Fatigue is an important FM symptom, and it is often
identification of at least 11 of a possible 18
multi-modal in cause. Chronic pain, non-restorative
OCCIPUT: bilateral, at the suboccipital muscle
LOW CERVICAL: bilateral, at the anterior aspects of
the intertransverse spaces at C5-C7.
TRAPEZIUS: bilateral, at the midpoint of the upper
border.
SUPRASPINATUS: bilateral, at origins, above the
scapula spine near the medial border.
SECOND RIB: bilateral, at the second costochondral
junctions, just lateral to the junctions on upper
surfaces.
LATERAL EPICONDYLE: bilateral, 2 cm distal to the
epicondyles.
GLUTEAL: bilateral, in upper outer quadrants of
buttocks in anterior fold of muscle.
GREATER TROCHANTER: bilateral, posterior to the
KNEE: bilateral, at the medial fat pad proximal to the
joint line.
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
sleep disturbances, autonomic nervous system
dysfunction, chronic anxiety and depression,
Myofascial pain is a big problem for many FM
exercise deconditioning, sedative effects of
patients. Patients with this condition get palpable
prescribed medications, and poor management of
"knots" in their muscles and soft tissues that cause
available energy can cause patients to be fatigued.
significant pain which at first glance may be mistaken
While sleep medications such as zolpidem (Ambien)
for painful muscle spasms. I have had patients
that induce sleep while preserving normal sleep
misdiagnosed as having fibrocystic breast disease who
architecture are effective in treating the fatigue of
really had tender myofascial nodules in their breast
fibromyalgia, they are not effective in treating FM
tissue that could be eliminated with massage therapy
pain for most patients.
techniques! I've seen orthopedic surgeons want to
The sleep abnormalities in FM are reproducible
operate on moderately severe osteoarthritis of the knee
in overnight sleep studies (this test may be ordered
when the real problem was severe myofascial pain
but is not necessary for the diagnosis of FM). One
around the knee that responded to medication and
sees alpha wave intrusion in delta sleep and a
physical therapy.
decrease in stage 3 and 4 sleep in many FM patients
Doctors of physical medicine and rehabilitation
(though these findings may not be present in treated
often describe myofascial pain as originating in painful
patients). These findings appear to be responsible
tissue which contains nodules associated with "trigger
for the non-restorative sleep and daytime som-
points" (not to be confused with the diagnostic "tender
nolence often described by those with fibromyalgia,
points" of fibromyalgia!) which are palpable, tense,
and they can also be seen in patients with
or taut bands of muscle and surrounding tissue. These
rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and Sjögren's
trigger points are often so painful that the patient is
syndrome as well as other illnesses.8
very uncomfortable. There can also be "latent triggerpoints" that the patient doesn't report as tender, but
can be very painful upon examination. Trigger points
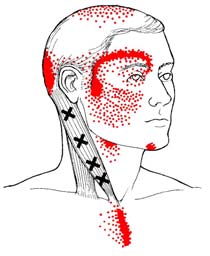
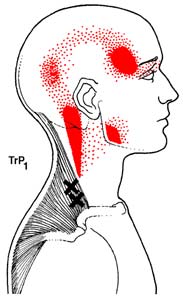
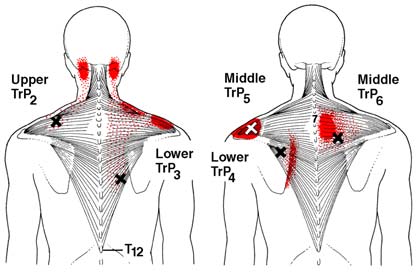
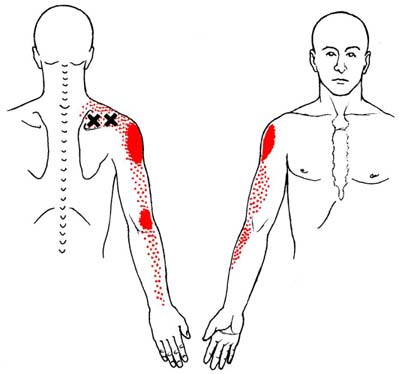
There is a growing body of scientific evidence which
are typically associated with a referred pain pattern,
suggests that a subset of FM patients have genetic
sometimes at distant sites from the primary pain source,
factors that predispose them to develop FM. Dr.
(See Figure 2) and are responsible for musculoskeletal
Arnold and colleagues showed that the first-degree
stiffness, weakness, and limitation of motion.
relatives of FM patients had an eight-fold greater risk
Scientific evidence has demonstrated that painful
of developing FM than did the general population.9
myofascial tissue has increased levels of the pain
These patients tend to have primary FM which has
neurotransmitters Substance P and glutamate as well
usually been present since the teenage years, though
as other mediators of pain and inflammation.12,13 Dr.
the symptoms may not be clinically apparent until the
Jay Shah at the NIH is involved in much of the recent
patient is exposed to significant physical or emotional
investigations into the pathophysiology of these
stressors. Secondary FM is usually secondary to an
palpable, hyperirritable nodules that cause myofascial
overwhelming infection, injury, or a significant pain-
pain.13 There appears to be an association between
generating problem that causes increased CNS pain
myofascial pain and low levels of Vitamin B12 and D
called central sensitization. Genetic abnormalities in
as well as iron deficiency, and these common
the serotonin transporter promoter gene have been
deficiencies should be treated if present in FM
noted in FM.10 Patients with adequate serotonin
transporter promoter genes seem to be lesssusceptible to the adverse effects of chronic stress
Autonomic Nervous System Abnormalities
and depressive events. Another gene, catecholamine-
There is research that suggests that autonomic
0- methyltransferase (COMT) has been shown to be
nervous system dysfunction, which includes
associated with pain regulation and myofascial pain
increased sympathetic tone, is an important factor
of the jaw, and there is an increased association of
in the pathophysiology of FM as well.14 FM
COMT deficiency in FM patients.11
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
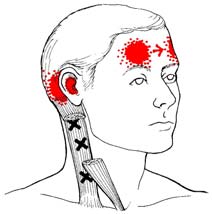
Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
patients commonly have autonomic nervous system
abnormalities that make them vulnerable tocoexistent conditions such as neurally-mediated
Examples Of
hypotension/reduced heart rate variability, irritablebowel and bladder syndromes, and vascular
headaches. Autonomic dysfunction may be partially
Points & Their
due to neuroendocrine abnormalities in the
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis foundin FM. Documented abnormalities include low AM
Zones Of Referred
cortisol and 24-hour urinary cortisol levels,
Pain In The Body*
inappropriately high levels of adrenocortical trophic
Trapezius Muscle Trigger Points
hormones (ACTH), and failure to suppress ACTHwith dexamethasone. The physician needs to beaware of the need to treat neurally-mediatedhypotension in FM patients with adequate salt andfluids as well as explaining the need for conservationof energy. If the hypotension is more severe,cardiac consultation for tilt table testing can berequested.
Central Sensitization, CNS "Windup" &
Trapezius Muscle Trigger Points
Hyperalgesia
The central nervous system is the major source of
pain in FM, and treatment of CNS pain is essential.
FM patients get a phenomenon called central
Supraspinatus Muscle
sensitization, the amplification of CNS pain
transmission and processing, that causes hyperalgesia(increased sensitivity to pain) and allodynia (painfulperception of normal situations). We now understandthat increased afferent pain pathways in the CNS areassociated with elevated levels of the neurotransmittersSubstance P and glutamate. There is also a reductionof pain modulating neurotransmitters (serotonin andnorepinephrine) in the descending CNS pain pathwaysthat normally dampen pain transmission. Theseabnormal changes occur in the dorsal horn of the spinalcord and contribute to the hyperalgesic state.
Functional brain MRI studies show increased painprocessing activity in the brain in response to noxiousstimuli in FM, confirming central sensitization.
Drs. Price and Staud have demonstrated that with
increasing nociceptive inputs, there is an increased
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Trigger Points
temporal summation of CNS pain discharges or"windup."15 This increased activity of the nociceptive
*Trigger points are marked by "X's" above. Pain referral
neurons in the spinal cord involves increased NMDA
zones are marked by solid blotches of dark ink with
receptor activity and neural plasticity of nociceptive
stippling showing spillover portions of pain.
spinal cord pathways, and it is an important factor in
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
central sensitization. The pain in FM is not due to
the physician use
inflammation, and traditional pain medications such
to assess the sta-
as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID's)
tus of the FM pa-
or corticosteroids which treat pain and inflammation
tient? First, it is
are not effective in treating FM pain.16
important for thephysician to see
Treatment of Fibromyalgia By The
the patient oftenuntil his or her
Patient's Primary Care Doctor
I've listed below some of the most commonly
prescribed treatments for FM. I've tried to emphasize
the patient keep a
the FDA- approved drugs and other evidence-based,
pain and activity
successful therapies. No one therapy is successful for
all FM patients. It is very important for physicians to
see patients on a regular basis and carefully determine
which therapies are most successful for each particular
her functional sta-
patient. Since patients often have multiple symptoms,
tus (activities of daily living, exercise, and work) and
it is important to treat FM holistically rather than treat
recording the patient's subjective pain score ( 0-10),
each symptom separately with a polypharmacy
the physician will have a better idea of how the patient
approach. However, since no one drug in clinical trials
appears to successfully treat FM in more than 50%
Important non-pain symptoms associated with FM
of cases, multiple drug therapy is necessary for many
usually include chronic fatigue, non-restorative sleep
FM patients.
disturbances and daytime somnolence, neurally-
Many FM patients have problems with multiple
mediated hypotension, cognitive dysfunction, irritable
chemical sensitivities. Part of the problem could be
bowel syndrome, increased anxiety, and reactive
due to how they metabolize or eliminate certain
depression (which is distinguished from major
medications. I often tell patients if they could tolerate
depressive disorder). In my clinical experience as a
the full dose of a prescribed drug their FM problems
rheumatologist who has treated FM patients for over
would be much less severe. Another problem is that
25 years, successful treatment of these other co-
the FDA-approved FM drugs were tested as
morbid FM problems is essential to a good clinical
monotherapies, meaning that patients were not
allowed to take other FM medications during the
It is also important to identify the patient's pain
clinical trials. Patients on more than one medication
generators. These pain generators can come from co-
can experience drug-drug interactions which require
existing osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic
them to use a lower dose of medication due to
lupus, myofascial pain, or other mechanical problems
increased side effects on the full dose. Some drugs
such as degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis.
have generic alternatives that may be absorbed
Adequate control of these additional sources of pain,
differently than the brand name drug. These problems
if present, is an important therapeutic challenge.
can often cause FM patients to have difficulty takingstandard doses of medication due to intolerable side
When a FM patient has a pain flare, it usually
effects. It is not uncommon for FM patients to need
involves a CNS windup and central sensitization. In
to start at lower than standard doses of medications.
my experience, it is essential to aggressively treat thistype of pain before it causes a chronic escalation ofthe patient's pain syndrome. It also gives the patient a
Medical Management For Fibromyalgia
sense of control and avoids unnecessary emergency
In addition to a tender points exam and an assessment
room visits. I encourage my patients to have adequate
of the patient's myofascial pain, range of motion,
pain medication at home for the short-term treatment
posture, and gait, what other diagnostic criteria should
of this type of emergency, breakthrough pain.
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
PHARMACOLOGY FOR FIBROMYALGIA
by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) . They
These drugs block the biogenic amines that are
also have TCA effects and are FDA-approved for
abnormal in the CNS in FM.
the treatment of moderate to severe pain. Clinical trials
a. Tricyclic Antidepressant Drugs (TCA): Bedtime
show them to be effective in the treatment of FM pain.
doses of low-dose amitriptyline (Elavil) and doxepin
My experience is that Ultracet is more effective than
(Sinequan) have been effective in FM.
Ultram with fewer adverse effects, and Ultram ERoffers the important benefit of 24-hour pain control
b. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI):
Only 40-80 mg. of fluoxetine (Prozac) has been
without breakthrough pain when the short acting drug
shown to be effective in small FM studies. The other
wears off in 6-8 hours.
SSRI's are effective in treating anxiety and depression,
b. Long-Acting Opioids: Fentanyl patch and time-
but not effective treating pain in FM studies.
release morphine have been shown to be effective for
c. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
long-term use in chronic low back pain and
(SNRI): Duloxetine (Cymbalta) and milnacipran
osteoarthritis pain, but their use should be limited to
(Savella) are now FDA-approved for the manage-
only the most severe chronic pain patients due to
ment of fibromyalgia. Cymbalta is also approved for
concerns about addictive potential and adverse effects.
the treatment of diabetic neuropathic pain, generalized
The EULAR (European League Against Rheumatism)
anxiety disorder, and major depressive disorder.
evidenced-based guidelines do not recommend these
Savella has a higher concentration of norepinephrine
drugs for the treatment of FM pain.17
than Cymbalta and may be more effective in the
c. Short-Acting Opioids: Hydrocodone and
treatment of FM fatigue. In clinical trials, both drugs
oxycodone, in combination with acetaminophen or
appear to be very effective in 30% of FM patients
ibuprofen, are excellent short-acting analgesics for
and partially effective in 50% of FM patients.
acute peripheral and CNS pain. They should not beused for chronic pain except in rare instances due toconcerns about addictive potential and adverse effects,
including the potential for withdrawal-related
(Calcium Channel Inhibitor Drugs) These drugs
symptoms of increased pain.
block the release of neurotransmitters Substance Pand Glutamate in hyper-excited nerve fibers.
4. MUSCLE RELAXANTS
a. Pregabalin (Lyrica) is now FDA-approved for
the management of fibromyalgia. It is also approved
Muscle relaxants are commonly used both chronically
for the treatment of shingles and diabetic neuropathic
and for acute pain flares in FM. Cyclobenzaprine
pain. In clinical trials, it appears to be very effective
(Flexeril) is effective in FM due to its tricyclic anti-
in 30% of FM patients and partially effective in 50%
depressant and muscle relaxant properties, and it is
of FM patients.
often used to help with sleep. There is now a 24-hour time release form of cyclobenzaprine, Amrix,
b. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is commonly used in the
which usually causes less sedation than cyclo-
treatment of FM and neuropathic pain. It is FDA-
benzaprine if used during the day.
indicated for shingles neuropathic pain and was shownto be effective for the treatment of FM in one clinicaltrial funded by the National Institutes of Health.
5. SEDATIVE HYPNOTICS
a. Non-Benzodiazepines: Zolpidem (Ambien) has
3. OPIOIDS
been shown to improve FM sleep disturbances andfatigue.
a. Tramadol (Ultram), Tramadol with Aceta-
minophen (Ultracet), and Tramadol Extended
b. Benzodiazepines: Alprazolam (Xanax) has been
Release (Ultram ER): are weak opioids, but they are
shown to be effective in FM.
not considered controlled substances as determined
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org


Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
NON-PHARMACOLOGIC TREATMENT FOR FIBROMYALGIA
1. EDUCATION:
When a FM diagnosis is made, and the condition
their pain (by increasing endorphins in the CNS),
is properly explained to the patient and family, the
mood, physical conditioning, and functional status.
intensity of symptoms will often be reduced by
It is important to combine exercise with adequate
one-third due to reduction in patient anxiety which
stretching as well as energy conservation to prevent
contributes to abnormal pain processing. An
injury or FM flare. I find core and Pilates exercises
essential goal of FM treatment is to empower the
as well as warm water aquatic exercises (when
patient to understand his or her illness and learn
possible) to be very effective for most of my FM
how to best manage the disease.
2. PHYSICAL THERAPY:
4. COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY &
Proper posture, balance, muscle tone, and
BEHAVIORAL MODIFICATION THERAPY:
physical conditioning are important needs to
These are being used in FM with increasing
correct in many FM patients, much more so than
frequency and success. Proper conservation of your
for their non-fibromyalgia friends with similar poor
available energy and development of coping skills
posture, muscle tone, and physical conditioning.
to reduce anxiety over dealing with chronic pain are
It is often necessary to prescribe physical therapy
important goals in the management of FM.
with a therapist skilled in FM, myofascial release,and neuromuscular re-education before the patient
can successfully progress to an appropriate
This discipline has been shown to be an effective
exercise program.
FM treatment in small clinical studies. It shouldbe considered a supplemental therapy for FM
3. EXERCISE:
patients and can be very beneficial in selected
Low impact, aerobic exercise is an important
treatment for almost all FM patients to improve
Important Note: Before attempting any new form of medication or treatment, be sure to check with your physician.
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
Fibromyalgia Frontiers • 2010 (Volume 18, Number 1)
June 23, 2003. Website: www.fda.gov/ oh rms/dockets/ac/03/transcripts/3967T1.htm , pp. 26-45.
As my experience treating FM patients grows, and thescience regarding the disease and treatment options
7) Williams DA and Gracely RH. Biology and therapyof fibromyalgia. Functional magnetic resonance
increases, I find myself becoming more and more
imaging findings in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Res Ther
optimistic about good patient outcomes. Most FM
2006; 8(6): 224.
patients have symptoms that do not worsen over time,
8) Arnold LM et al. Family study of fibromyalgia.
and many patients improve to a level of pain they can
Arthritis Rheum 2004 Mar;50(3):944-52
tolerate and be functional. The mainstay of treatment is
9) Drewes AM. Pain and sleep disturbances with
the use of evidence-based treatments which include
special reference to fibromyalgia and rheumatoid
patients' active participation to fine tune their treatment
arthritis. Rheumatology 1999 Nov;38(11):1035-8.
plans to their particular needs, as part of the medical
10) Buskila D, Neumann L, Epstein RP. Confirmation of
team. This formula ensures a successful and positive
an association between fibromyalgia and serotonin
relationship for both doctor and patient.
transporter promoter region (5-HTTLRPR)polymorphism, and relationship to anxiety-relatedpersonality traits. Arthritis Rheum 2002 Mar;46(3):845-7.
Dr. Rothenberg is Board Certified in
Rheumatology and Internal Medicine and
11) Gursoy S, Erdal E, Herken H, Madenci E, Alasehirli B,
is Chair of the Medical Advisory Board of
Erdal N. Significance of catecho-O-methyltransferase
the National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc.
gene polymorphism in fibromyalgia syndrome.
He is in private practice in Bethesda, MD.
Rheumatol Int 2003 May;23(3):104-7.
You can contact him at:
12) De Stefano R, Selvi E, Villanova M., et al. Imageanalysis quantification of substance P immunoreactivity
The Camalier Building
in the trapezius muscle of patients with fibromyalgia and
10215 Fernwood Road, Suite 401
myofascial pain syndrome. J Rheumatol 2000;27(12):
Bethesda, MD 20817-1106
Telephone: (301) 571-2273
13) Shah J et al. Biochemicals associated with pain andinflammation are elevated in sites near to and remotefrom active myofascial trigger points. Arch Phys MedRehabil 2008 Jan;89(1):16-23.
14) Martínez-Lavín M. A novel holistic explanation forthe fibromyalgia enigma: autonomic nervous systemdysfunction. Fibromyalgia Frontiers 2001; Vol 10(1).
1) Smythe HA, Moldofsky H. Two contributions to under-standing the "fibrositis" syndrome. Bull Rheum Dis 1977-
15) Price D and Staud R. Neurobiology of fibromyalgia
syndrome. J Rheumatol Suppl 2005 Aug;32(75):22-8.
2) Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The American
16) Mease P. Fibromyalgia syndrome: review of clinical
College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the classification
presentation, pathogenesis, outcome measures and
of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1990 Feb;33(2):160-72.
treatment. J Rheumatol 2005;32(75):6-21.
3) Goldenberg DL, Simms RW, Geiger A, Komaroff AL. High
17) Carville SF et al. EULAR evidence-based
frequency of fibromyalgia in patients with chronic fatigue
recommendations for the management of fibromyalgia
seen in a primary care practice. Arthritis Rheum 1990 Mar;
syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis July 20, 2007; dol, p.1522.
4) Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J. The prevalence andcharacteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population.
This article may be photocopied in its
Arthritis Rheum 1995 Jan;38(1):19-28. Also,Weir PT, et al. J
entirety, and distributed without per-
Clin Rheumatol 2006 Jun;12(3):124-8.
mission, if used for non-commercial,
5) Ibid. Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The
educational purposes. It may not be
American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the
reprinted or reproduced in any publi-
classification of fibromyalgia.
cation, website, or other media without
prior permission.
6) Bradley L. FDA Center for Drug Evaluation andResearch, Meeting of the Arthritis Advisory Committee,
National Fibromyalgia Partnership, Inc. (NFP). • www.fmpartnership.org
Source: http://russellrothenbergmd.com/pdf/fibro2.pdf
MITCHEL PAUL GOLDMAN 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 300 ; San Diego, California 92121 (Phone: 858-657-1002) (Fax: 858-657-9165) E-Mail: [email protected] BORN: APRIL 5, 1955 (MIAMI BEACH, FLORIDA) EDUCATION Sept 1973 - Jan 1977 Boston University College of Liberal Arts - Biology B.A. 1977 Sept 1978 - June 1982 Stanford University
An Information Brochure by The Gut Foundation Diverticular diseaseWhat is it?Diverticular disease affects the large bowel. The disease is usually confined to the sigmoid colon although it can involve all the colon. Diverticula are small pockets or sacs that protrude beyond the wall of the bowel and vary in size from that of a pinhead to a small grape. The mouth of the diverticulum is often narrow giving it a teardrop shape. The local bowel wall is thickened.











