Viagra gibt es mittlerweile nicht nur als Original, sondern auch in Form von Generika. Diese enthalten denselben Wirkstoff Sildenafil. Patienten suchen deshalb nach viagra generika schweiz, um ein günstigeres Präparat zu finden. Unterschiede bestehen oft nur in Verpackung und Preis.
The effects of enalapril and losartan on mechanical ventilation-induced sympathoadrenal activation and oxidative stress in rats


Available online at
journal home page:
The effects of enalapril and losartan on mechanicalventilationeinduced sympathoadrenal activationand oxidative stress in rats
Hale Zerrin Toklu, PhDOh-Sung Kwon, Yasemin Saka,Scott K. Powers, Katherine Llinas,Nataliya Kirichenko, MSc,Kurt J. Sollanek, Michael P. Wiggs, Ashley J. Smuder, Erin E. Talbert, Philip J. Scarpace, PhD,and Nihal Tu¨mer,
a Malcom Randall Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center, Gainesville,Floridab Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, Floridac Department of Pharmacology, Marmara University School of Pharmacy, Istanbul, Turkeyd Department of Applied Physiology and Kinesiology, College of Health & Human Performance, University of Florida,Gainesville, Florida
Background: Mechanical ventilation (MV) is a method of maintaining appropriate gas ex-
Received 1 November 2013
change in patients who are unable to sustain adequate alveolar ventilation. While life-
Received in revised form
saving in the short-term, prolonged MV leads to altered cardiovascular responses and
enhanced lung injury, but the exact mechanism is unknown. Therefore, we investigated
Accepted 30 January 2014
the involvement of the sympathoadrenergic and renineangiotensin system in MV-induced
Available online xxx
altered cardiovascular responses.
Methods: SpragueeDawley rats were divided into six groups: (1) spontaneous breathing (SB);
(2) SB þ enalapril (100 mg/kg intravenous infusion); (3) SB þ losartan (100 mg/kg infusion); (4)
Mechanical ventilation
12 h of MV; (5) MV þ enalapril; and (6) MV þ losartan. After the animals were sacrificed,
blood and tissue samples were collected. Tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine beta hydroxy-
lase, and neuropeptide Y were measured in adrenal medulla and hypothalamus, whereas
AT1 was measured in lung tissues by Western blot. Norepinephrine enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay and total antioxidant capacity were assayed in plasma.
Thyrosine hydroxylase
Results: Our findings indicated that MV increases the sympathetic activation markers in ad-
Dopamine beta hydroxylase
renal medulla and hypothalamus. Moreover, oxidative stress was increased in lung and brain
tissues. Treatment with enalapril or losartan reduced the lipid peroxidation in lung and brain
tissues, while preserving the tissue glutathione content and plasma antioxidant capacity.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that the inhibition of the renineangiotensin system byenalapril or losartan may reduce the MV-induced increase in sympathetic activity markersand oxidative stress, and thus, may have a beneficial effect as adjuvant therapy.
ª 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
* Corresponding author. Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, College of Medicine, University of Florida, P.O. Box 100267,
Gainesville, FL 32610.
** Corresponding author. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, College of Medicine, University of Florida, P.O. Box 100267, Gainesville, FL 32610.
E-mail addresses: (H.Z. Toklu), (N. Tu¨mer).
0022-4804/$ e see front matter ª 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
treated with the AT1 antagonist losartan; (4) 12 h of MV; (5)12 h of MV with the ACE inhibitor enalapril; and (6) 12 h of MV
Mechanical ventilation (MV) is a method to mechanically
with the AT1 antagonist losartan.
assist or replace spontaneous breathing (SB). Although it is
Losartan group received an intraperitoneal priming dose
often a lifesaving intervention in critically ill patients, it
(30 mg/kg) followed by intravenous infusion (100 mg/kg/min,
carries many potential complications including pneumo-
infusion rate 0.30 mL/h), and enalapril group received
thorax, acute lung injury, and ventilator-associated pneu-
enalapril (40 mg/kg) followed by an intravenous infusion
monia. Other complications include diaphragm atrophy,
(100 mg/kg/min, infusion rate 0.30 mL/h) while during the 12 h
decreased cardiac output, and oxygen toxicity . The in-
flammatory response in the lungs due to MV may lead to distalorgan dysfunction.
Experimental protocol
Recent research indicates a cross talk between lungs and
other organs, including brain hypothalamic sym-
Animals were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital
pathoadrenal medullary axis leads to marked activation of the
(60 mg/kg, intraperitoneally). After reaching a surgical plane of
adrenal medulla and sympathetic ganglia characterized by
anesthesia, tracheostomy was performed on the animals
elevated activity of the catecholamine biosynthesizing en-
using aseptic techniques and mechanically ventilated with a
zymes such as tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine beta
controlled pressure-driven ventilator (Servoventilator 300;
hydroxylase (DbH), resulting in a rise in circulating epineph-
Siemens; Bridgewater, NJ) for 12 h with the following settings:
rine and norepinephrine (NE). TH is the rate-limiting step
upper airway pressure limit, 20 cm H2O; pressure control level
in catecholamine biosynthesis as it catalyzes the hydroxyl-
above positive end-expiratory pressure 4e6 cm H2O; respira-
ation of tyrosine to dopamine, whereas DbH catalyzes the
tory rate, 80 beats/min; and positive end-expiratory pressure
conversion of dopamine to NE. In addition to catecholamines,
1.0 cm H2O. In general, we estimate that these ventilator
neuropeptide Y (NPY) is synthesized in the adrenal medulla
settings result in a tidal volume of w1 mL/100 g of body
and is co-released with epinephrine and NE. The previously
weight. All surgical procedures were performed as previously
mentioned factors, TH, DbH, and NPY are considered as bio-
described in detail Briefly, cannulas were inserted into
markers of sympathetic nervous system activity .
the carotid artery to permit continuous measurement of blood
Sympathoactivation contributes to systemic stress and
pressure and the collection of periodic arterial blood samples
cardiovascular complications. The patients who have pro-
during MV. Blood samples were analyzed for pH, pO2, and
longed MV display blood pressure alterations and abnormal
pCO2 using an electronic blood gas analyzer (GEM Premier
autonomic responses which may be because of MV-
3000; Instrumentation Laboratory; Lexington, MA). If neces-
associated activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
sary, adjustments were made to the ventilator to ensure that
axis or hypothalamic sympathoadrenal medullary axis.
the arterial blood gas and pH measures were within the
Whether MV activates these axis is unknown.
desired physiological ranges. PaO2 was maintained at 70 mm
The present study was aimed to test the hypothesis that a
Hg throughout the experiment by adjustments in FiO2 (22%e
12 h exposure to MV results in increased activation of the
25% oxygen). Cannulas were inserted into the jugular vein for
hypothalamic sympathoadrenal medullary axis besides
the constant infusion of sodium pentobarbital (w10 mg/kg/h).
increasing oxidative stress in plasma and other organs. Thus,
Body temperature was maintained between 36�C and 37�C by
we measured TH, DbH, and NPY protein expression in the
using a recirculating heating blanket. Continuous care during
adrenal medulla and hypothalamus, lung angiotensin II type 1
the MV protocol included lubricating the eyes, expressing the
(AT1) receptor protein levels, oxidative stress in lung and
bladder, removing airway mucus, rotating the animal, and
brain, and plasma NE. In addition, the effects of enalapril-
passive limb movement. After 12 h of MV, the animals were
angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE) and losartan-
immediately killed, and blood and tissue samples were
AT1 receptor blocker on MV-induced changes were evaluated.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Materials and methods
measurements of plasma NE
Blood samples were taken via cardiac puncture at the time ofsacrifice and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min at 4�C. The
Adult female SpragueeDawley rats were obtained from
samples were stored at �80�C until further analysis by an
Charles River Labs and were aged 4e6 mo and w300 g at the
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (Rocky Mountain
time of sacrifice. All animals were housed at the University of
Diagnostics, Inc Colorado Springs, CO) following the in-
Florida Animal Care Services Center according to the guide-
structions of the manufacturer.
lines set forth by the Institutional Animal Care and UseCommittee. Animals were maintained on a 12-h lightedark
Total antioxidant capacity in the plasma
cycle and provided food (AIN93 diet) and water ad libitumthroughout the experimental protocol. Animals were divided
Total antioxidant capacity in the plasma was evaluated by
into six groups (10 animals/group) as follows: (1) 12 h of SB; (2)
Oxiselect kit (Biocell Laboratories, San Diego, CA) according to
SB group treated with the ACE inhibitor enalapril; (3) SB group
the manufacturer's instructions.
Table e Plasma total antioxidant capacity (tAOC) expressed as copper reducing equivalent (CRE) and NE concentrations inSB, enalapril, losartan, and MV groups at 12 h. Each group consists of six to eight rats.*P < 0.05 versus SB and D P < 0.05
versus MV. Values are presented as mean ± standard error of mean.
Plasma concentration
tAOC (CRE mmol/mL)
MVE ¼ MV with the ACE inhibitor enalapril; MVL ¼ MV with the AT1 antagonist losartan; SBE ¼ SB group treated with the ACE inhibitor enalapril;SBL ¼ SB group treated with the AT1 antagonist losartan.
Tissue preparation
followed by Tukey multiple comparison test or Student t-testusing a GraphPad Prism 5.0 software (GraphPad, San Diego,
After completion of the experimental protocol, animals were
CA). Significance was established at P < 0.05.
overanesthetized with pentobarbital (120 mg/kg intraperito-neally) and the adrenal medulla, hypothalamus, and lungrapidly removed, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and
stored at �80�C until subsequent analyses. Before homoge-nization, adrenals were decapsulated and the medullae were
MV caused a decrease in the total antioxidant capacity of the
separated from the cortex.
plasma in MV group. Enalapril and losartan treatmentssignificantly restored the plasma antioxidant capacity ).
Western blot analysis
Moreover, the plasma NE levels had a tendency to decrease
in the MV group; however, this decrease was not significant
Adrenal medulla, hypothalamus, and lung were homogenized
because of the large variation between samples. Treatment
and assayed for protein levels of the catecholamine biosyn-
with enalapril or losartan prevented this decrease ).
thetic enzymes, TH and DbH, along with NPY using antibodies
MV caused an increase in sympathetic activation markers,
directed to TH (1/8000; Pel-Freez Biologicals, Rogers, AR), DbH
that is, TH, DbH, and NPY in adrenal medulla, therapeutic
(1/2000; Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO), NPY (1/500; Santa
intervention with either enalapril or losartan reversed these
Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), and AT1(1/2000; Abcam,
MV-induced changes ). In contrast, TH remained un-
Cambridge, MA). All secondary antibodies were used in a
changed in hypothalamus, whereas DBH and NPY were
concentration of 1/2000). An equal amount of protein for each
elevated with MV. In the hypothalamus, enalapril failed to
adrenal medulla homogenate (2 mg protein for TH, 10 mg for
inhibit the increases in DbH and NPY while losartan had effi-
DbH, and 35 mg for NPY), hypothalamus homogenate (4 mg
protein for TH, 0.2 mg protein for DbH, and 40 mg for NPY), and
AT1 protein was assessed in the lungs. AT1 receptor pro-
lung (40 mg protein for AT1) was applied to the gels.
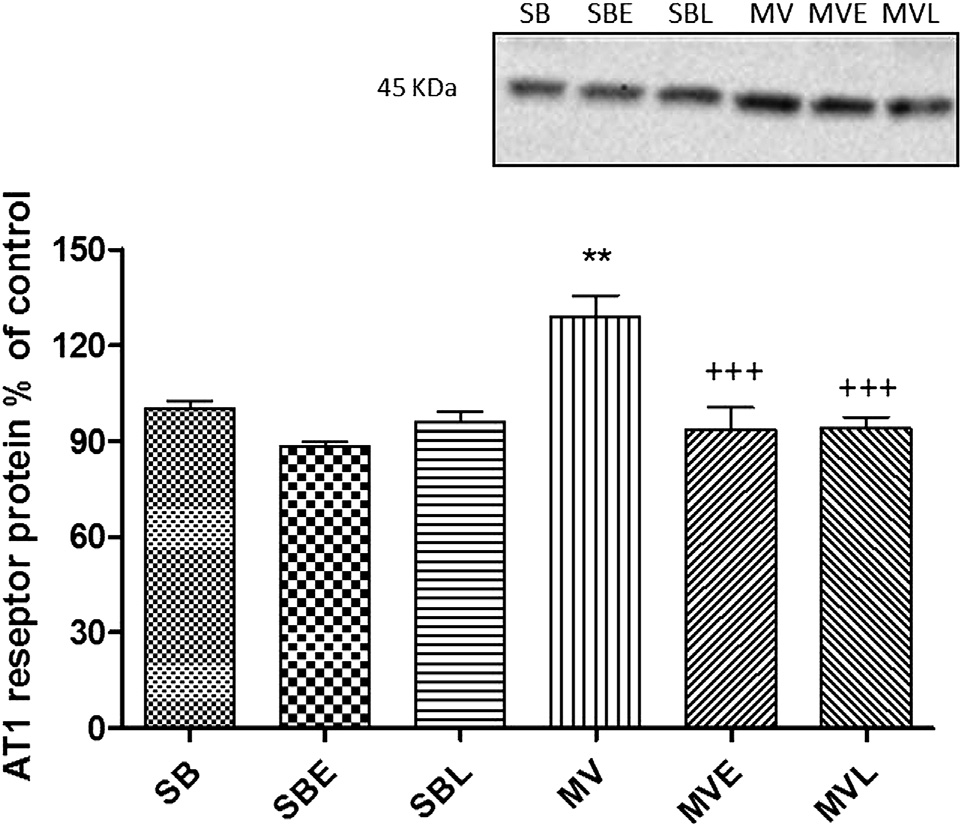
tein was elevated with MV, and although there was no changewith drug treatment in the absence of MV, enalapril and los-
Malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH)
artan reversed the MV-induced increase
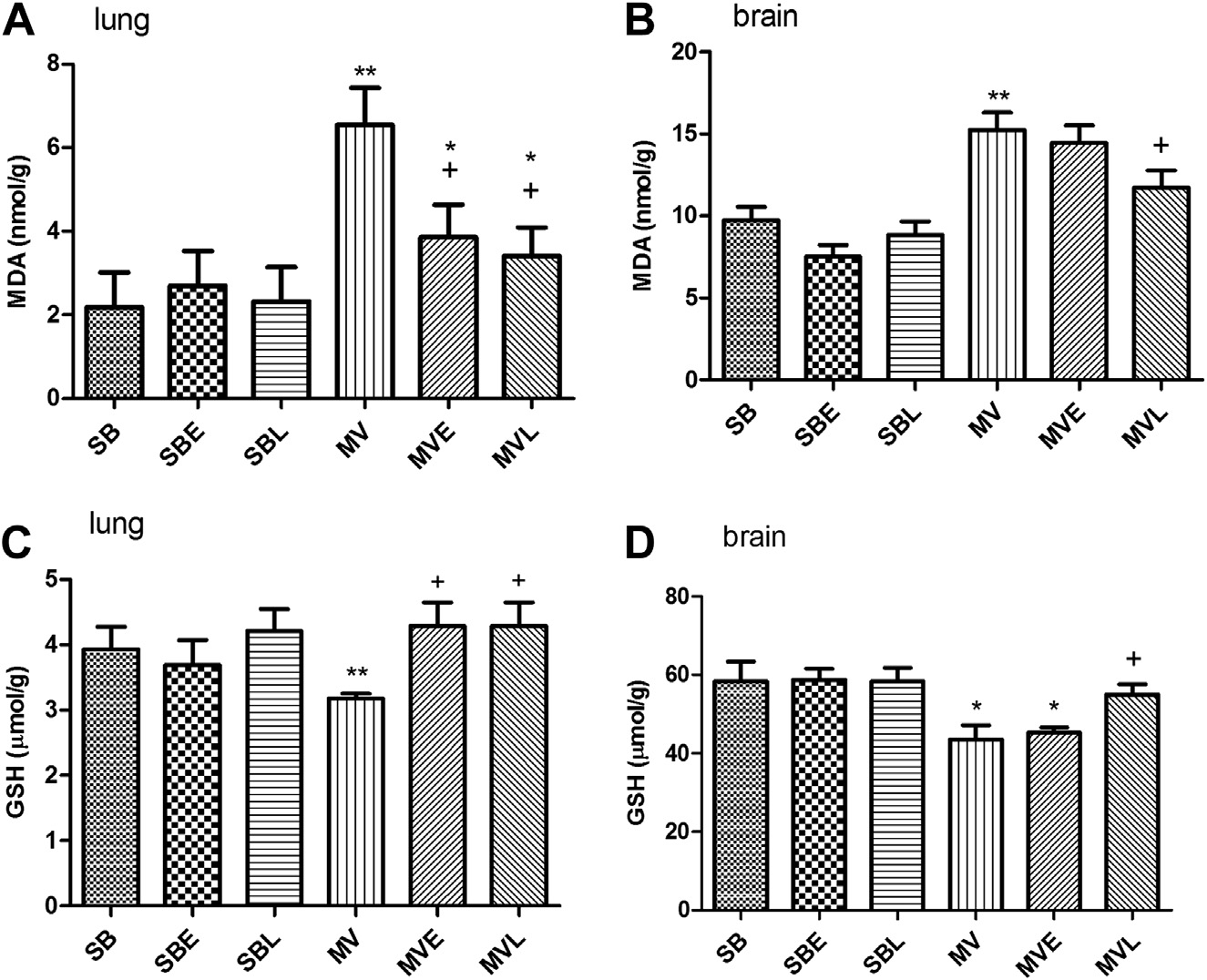
MV caused an increase in both lung and brain tissues lipid
peroxidation as evidenced by the increase in the malondial-
Tissue samples were homogenized with potassium phosphate
dehyde content, that is, thiobarbituric acid reactive substance.
buffer (pH 6.0) and ice-cold trichloroacetic acid (1 g tissue plus
Also there was a concomitant decrease in GSH content in
10 mL 10% trichloroacetic acid) in an ultrasonic tissue ho-
these tissues. Treatment with either enalapril or losartan
mogenizer. The MDA levels were assayed for products of lipid
prevented the decrease in GSH and reduced the lipid peroxi-
peroxidation by monitoring thiobarbituric acid reactive sub-
stance formation as described previously Lipid peroxida-tion is expressed in terms of MDA equivalents using anextinction coefficient of 1.56 � 105 /M/cm and the results are
expressed as nmol MDA/g tissue.
GSH measurements were performed using a modification
MV not only causes an injury in the lung, but also may lead to
of the Ellman procedure Briefly, after centrifugation at
oxidative stress and injury in distant organs It is known
2000g for 10 min, 0.5 mL of supernatant was added to 2 mL of
that there are a multiple pathways enabling cross talk be-
0.3 mol/L Na2HPO4 2H2O solution. A 0.2 mL solution of dithio-
tween lung and other organs including the brain. An insult to
bisnitrobenzoate (0.4 mg/mL 1% sodium citrate) was added,
the lung may alter physiological factors and may lead to an
and the absorbance at 412 nm was measured immediately
imbalance in the brain. Because the integrity of the brain
after mixing. The results are expressed in mmol GSH/g tissue.
function mainly depends on O2 and glucose, a peripheral ho-meostatic imbalance likely triggers an inflammatory response
through cytokines and other mediators .
Previous reports have shown that MV increases the
Data are presented as mean � standard error of mean. Com-
oxidative stress and causes ventilation-induced acute lung
parisons between groups were done by analysis of variance
injury and secondary injuries in other organs such as
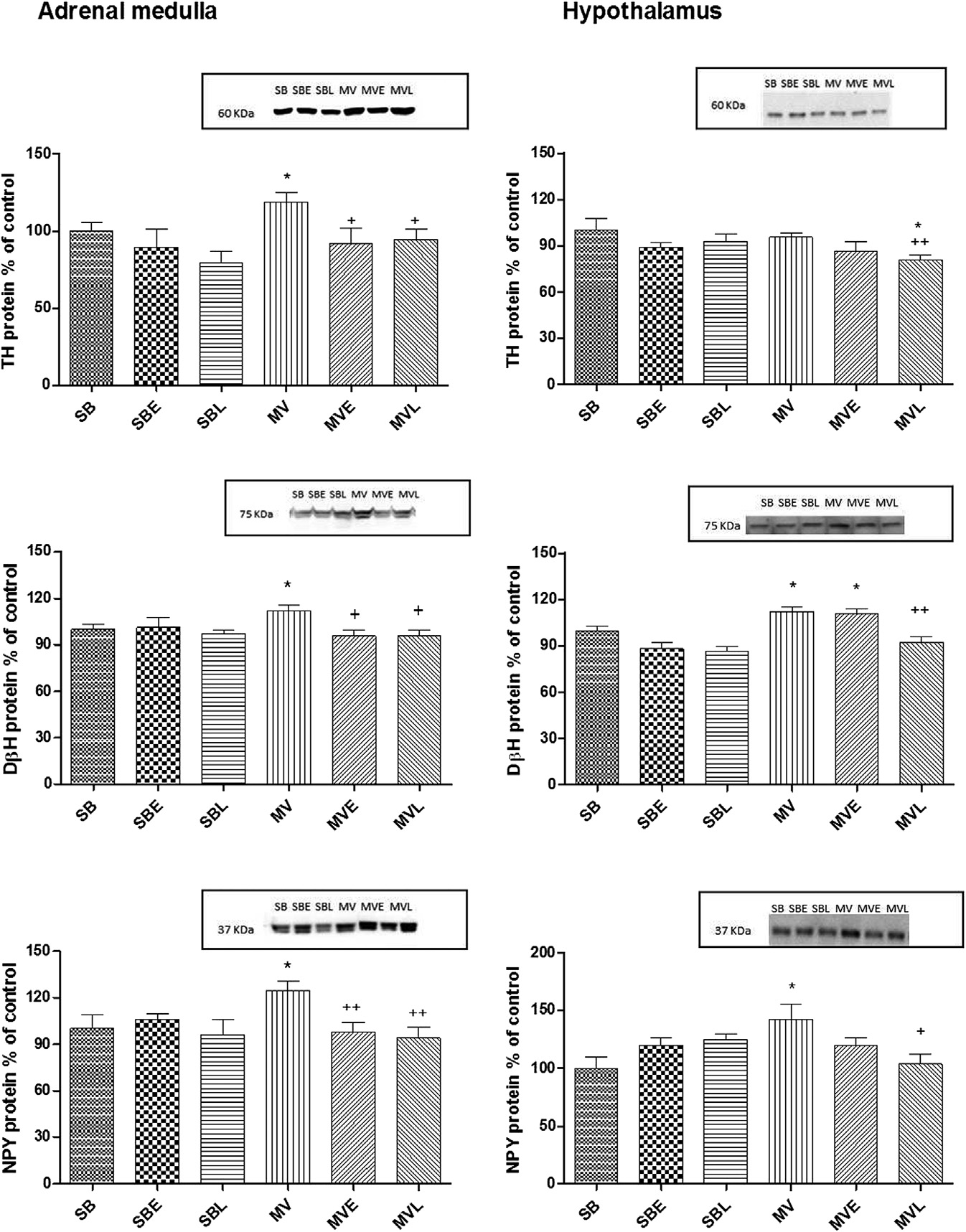
Fig. 1 e Western blot analysis of the protein levels of TH, DßH, and NPY in the adrenal medulla and hypothalamus tissues ofthe saline or enalapril (E) or losartan (L)-treated SB or MV groups. Each group consists of n [ 6e8 rats. *: P < 0.05 versus SBand D: P < 0.05 versus MV.
diaphragm, heart, or kidney It has been also shown
enalapril. Although both losartan and enalapril do not have a
that MV leads to a decrease in tissue GSH levels In the
sulfhydryl moiety have previously been shown to exert anti-
present study, we have consistently observed that MV caused
oxidant effects in various studies Therefore, our
a decrease in GSH levels in lung and brain, and a concomitant
finding that losartan and enalapril reduce oxidative stress and
increase in lipid peroxidation as evidenced by the increase in
increase antioxidant capacity was consistent with these pre-
the malondialdehyde content, a thiobarbituric acid reactive
vious reports . However, the failure of enalapril to protect
substance. Moreover, plasma antioxidant capacity was
brain tissue could be a result of its inability to cross the blood
decreased probably because of the extensive oxidative stress
brain barrier. For instance, it has been claimed that losartan
in the body. GSH is one of the principle endogenous antioxi-
effects are limited to the periphery except for the cases with
dants in all tissues, and the oxidative injury is a consequence
brain injury On the other hand, there are several studies
of GSH depletion . Therefore, antioxidants and GSH ana-
that support the central effects of losartan. Kucuk et al.
logs have been widely studied to prevent or reduce oxidative
showed that losartan treatment attenuated hypertension-
injury in various models.
induced bloodebrain barrier permeability. Moreover, func-
In the present study, both losartan and enalapril were
tional evidence has been shown that systemic administration
effective in reducing lipid peroxidation and partially in
of losartan crosses bloodebrain barrier in the rat and
preserving the GSH content in lung. On the other hand, in
attenuates the pressor response to electrical stimulation of
the brain, losartan demonstrated similar results, but not
subfornical organ .
losartan had some efficacy. This increase in the protein levelsof the biosynthetic enzymes (TH and DbH) was probablybecause of a compensatory mechanism to restore NE plasmalevels; we observed that plasma NE levels tended to decreaseat 12 h after MV.
The alteration of plasma epinephrine and NE levels
because of MV was previously reported by several researchers.
Aneman et al. showed NE was inconsistent or unstable inpatients. Monteverde showed that the NE requirementwas increased in pediatric patients in prolonged MV andBarbieri et al. showed that the plasma epinephrine and NEincreased at the first hour of MV in patients, and this increasewas restored to baseline levels by the termination of MV.
Moreover, Wieske et al. have proposed that the autonomicdysfunction caused abnormal heart rates in intensive careunit patients.
Activation of angiotensin system contributes to several
pathophysiological effects in the cardiovascular system via theactivation of sympathetic nervous system .Previous studies
Fig. 2 e Western blot analysis of the protein levels of AT1
have reported an increase in lung or bronchoalveolar fluid
receptor in the lung tissues of the saline or enalapril (E)-or
angiotensin II levels at 2 or 4 h of MV However, lung
losartan (L)-treated SB or MV groups. Each group consists
ACE levels were found to be unchanged or increased in
of n [ 6e8 rats. **: P < 0.01 versus SB and D: P < 0.05
bronchoalveolar fluid . Moreover, captopril was effective in
reducing the MV-induced lung injury and elevated ACE activity,and blockade of bradykinin receptors did not attenuate theeffect of captopril. Moreover, the serum ACE levels were un-
MV caused an increase in sympathetic activation markers,
changed, although angiotensin II levels were increased in the
that is, TH, DbH, and NPY in adrenal medulla. Although TH
bronchoalveolar fluid. Thus, indicating the role of a non-ACE
remained unchanged in hypothalamus, DbH and NPY were
pathway for the production of angiotensin II
elevated. Both drugs (enalapril and losartan) reversed these
A recent study has also shown that angiotensin 1e7 ana-
MV-induced changes in the adrenal medulla. However, ena-
logs protected the lung against acute lung injury, thereby
lapril failed to inhibit the increase in DbH and NPY while
increasing the ratio of ACE2/ACE activity and reducing the
Fig. 3 e Malonedialdehyde and GSH levels in lung (A and C) and brain (B and D) tissues of the salineorenalapril (E) or losartan(L)-treated groups. Each group consists of n [ 6e8 rats. *: P < 0.05 versus SB and D: P < 0.05 versus MV.
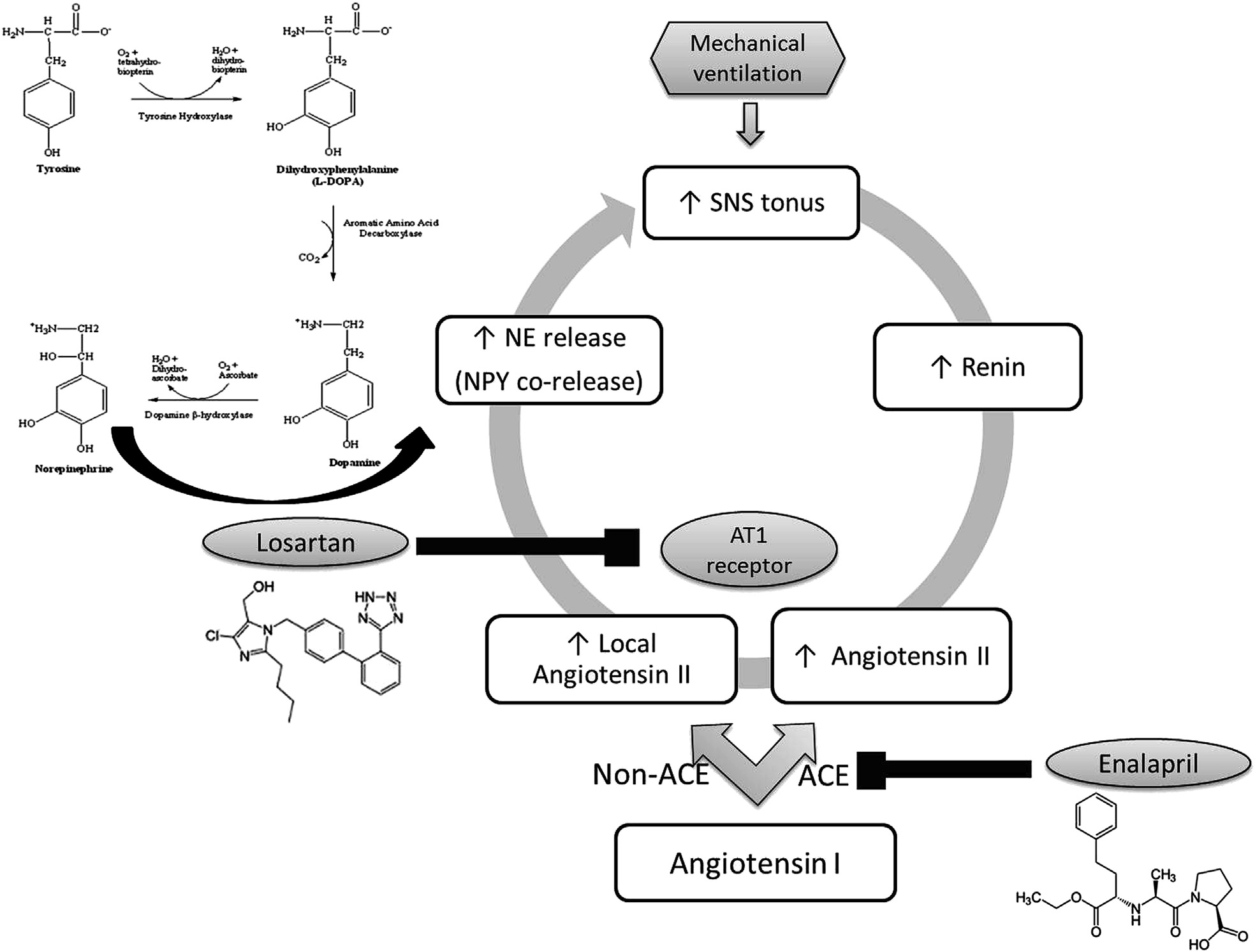
Fig. 4 e Mechanical ventilation increases the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) tonus as a result of increasednorepinephrine (NE) turnover. The levels of biosynthetic enzymes, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine betahydroxylase (DßH) are increased, along with an increase in NPY, which is co-released with NE. Sympathoactivation alsoactivates the renin-angiotensin system.
bioavailability of angiotensin II and AT1 receptor actions .
Increased angiotensin or AT1 levels have been correlated with
the severity of the injury. Both receptor types AT1 and AT2 inthe lungs were also shown to increase after MV . Similar
In summary, these data, for the first time, demonstrate that
to treatment with ACE inhibitors, treatment with an angio-
inhibition of renineangiotensin system by enalapril or los-
tensin receptor blocker, losartan, has been shown to reduce
artan may reduce the MV-induced increase in sympathetic
the lung edema, inflammation, and injury score and AT1 re-
activity markers and oxidative stress, and thus, may have a
ceptor messenger RNA because of MV
beneficial effect as adjuvant therapy.
In the present study, we did not measure the ACE activity
On the other hand, in humans and a number of species,
but we found that lung AT1 receptor protein was increased
including the hamster, quantitatively important chymase-
in the lung at 12 h of MV, and both enalapril and losartan
independent Ang II formation from Ang I occurs in the
treatments were effective in preventing this increase. As we
heart, arteries, and kidney. However, chymase differs in rats
previously discussed, both treatments also reduced the
and rabbits and is not active in the conversion of Ang I to Ang
oxidative stress in the lungs and sympathetic nervous sys-
II, but is involved in Ang II degradation. Consequently, one
tem activity markers in the adrenal medulla. On the other
would anticipate that blockade of the system at the ACE step
hand, it would have been valuable to evaluate the AT1 re-
in rats would be equivalent to inhibition of the Ang II receptor
ceptor protein in the aorta and to evaluate the sympathetic
in humans. On the other hand, AT1 receptor blockers may be
nervous system activity in different brain regions other than
more effective than ACE inhibitors in humans
Although the preliminary data of this study are important
to in terms of showing the involvement of the interaction of
renineangiotensin system with the MV-induced sympathetic
activation further studies are needed to elucidate the
detailed mechanisms and implement it into the clinical
This work was supported by the Medical Research Service of
the Department of Veterans Affairs. The authors declare that
they have no conflict of interest.
Author contributions: H.Z.T. collected the data, performed
statistical analysis, and prepared the manuscript. O-S.K.
adapted the animal model, performed the surgery, and
collected the data. Y.S., K.L., and N.K. collected the data and
performed analysis. K.J.S., M.P.W., A.J.S., and E.E.T performed
the surgery, follow up the animals, and collected the data. S.P.,
P.J.S., and N.T. were responsible for experimental design and
prepared the manuscript.
The authors reported no proprietary or commercial interest in
any product mentioned or concept discussed in this article.
Source: http://pilarmartinescudero.com/AbrilMayoJunio2014/Effects-enapril-losartan%20in%20ventilation%20exercise.pdf
Published online: August 31, 2015 Stress-response balance drives the evolution of anetwork module and its host genome Caleb González1,†, Joe Christian J Ray1,2,†, Michael Manhart3,4, Rhys M Adams1, Dmitry Nevozhay1,5, Alexandre V Morozov3,6 & Gábor Balázsi1,7,8,* have expanded quickly, feeding on general biological knowledge.Conversely, synthetic biology has enormous but unexploited poten-
Programa de Atención Cardiovascular de Emergencia Wanda Miranda Territory Director, ECC Programs Latin America The Caribbean, Spain and Portugal Información de Contacto Tel: +1-787-810-7920 Email: [email protected] ¿Quiénes somos? Cursos para la comunidad Cursos para el equipo de salud









