Viagra gibt es mittlerweile nicht nur als Original, sondern auch in Form von Generika. Diese enthalten denselben Wirkstoff Sildenafil. Patienten suchen deshalb nach viagra generika schweiz, um ein günstigeres Präparat zu finden. Unterschiede bestehen oft nur in Verpackung und Preis.
Untitled
Sri Lanka
Volume 6 No 03 ISSN:1800-4881 July-Sept 2013
Department of Animal Production and Health, P.O.Box 13, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
[email protected]
Anti Microbial Resistance
1.
Anti Microbial Resistance
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Mechanism of AMR
2 Status of Livestock Diseases
Antimicrobial agents are specific drugs used to treat
2.1 Bovine Disease
infections caused by bacteria in particular. It is an essential
2.1.1 Bovine Babesiosis
medicine for both animal and human health. Therapeutic
2.1.2 Bovine Brucellosis
use of Antibiotics in infected animals can make the
2.1.3 Black Quarter
difference between cure and death. They are invaluable, but some bacteria have demonstrated full or partial resistance
Foot and Mouth Disease
to different microbial agents to which it originally was
sensitive. This phenomenon is called Anti Microbial
2.2 Caprine Diseases
Resistance (AMR). Under such situation the standard anti
2.2.1 Contagious Pustular Dermatitis (CPD)
microbial treatments become ineffective and infections may
2.3 Poultry Diseases
persist increasing risk of spread.
The evolution of resistant strains is a natural phenomenon
2.3.2 Gumboro Disease
that happens when micro-organisms are exposed to
2.3.3 Newcastle Disease
antimicrobial agents, and resistant traits can be exchanged
2.3.4 Salmonellosis
between certain types of bacteria. Misuse of antimicrobial medicines accelerates this natural phenomenon and poor
3.
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
infection control practices encourages the spread of AMR.
3.1 National HPAI Surveillance Programme
Potential AMR public health risk can be associated with the
3.2 Global Distribution of Notifiable Avian
use of Antibiotics in food producing animals. Furthermore
many emerging infectious diseases are due to circulation of
3.3 Global situation of HPAI outbreaks.
novel clones of drug resistant bacteria.
Human and animal share the same micro-organisms and 60% of the recently emerging diseases are of animal origin. It is a key component in concern in both animal and public health today. Appropriate use of anti microbial agents is a critical issue in animal welfare, food safety and food security policies too. Therefore it is important to control the use of Antimicrobial agents in animal population; strictly restricting the use through Veterinarians whose ethics is guarantied by a Veterinary statutory body as laid down by law.
1.2 Mechanism of AMR
Therapeutic use of antibiotics in human medicine started as far as year 1940 and the first resistance was noted in late 1950s. Antibiotics have been reported to be used routinely in Veterinary medicine and Agriculture since 1950s. By 1960s the strains of
Salmonella enterica emerged in Europe and USA, resistant to commonly used antibiotics causing clinical diseases in calves and it was considered as a public health risk. Micro-organisms are present everywhere and can adapt to survive in extreme conditions like heat, cold, radioactivity etc. In contact with antibiotics, sensitive bacteria will get destroyed and the resistant will survive and develop.
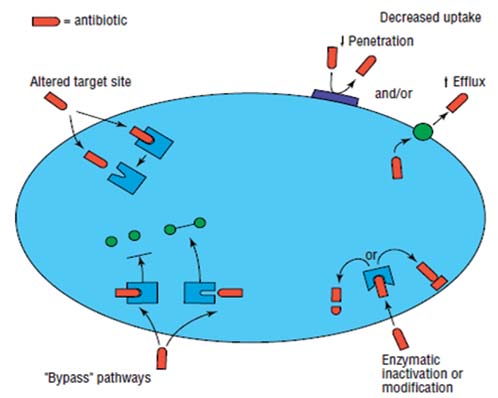
Therefore any use of antimicrobial will lead to the selection
Multi-drug resistant clones of Strptococcus pnuemoniae
of resistant bacteria. Bacteria have an ability to exchange
in circulation around the world that cause pneumonia,
genetic material and an ability to multiply. The higher the
ear infection and meningitis and multi-drug resistant
capacity of these characters the higher the adaptability. uropathogenic Eschrchia coli are becoming common in
The protection mechanisms have developed in bacteria human and animal health.
via genetic alterations to be able to survive to antibiotics
in the ecosystem. Genetic alterations occur either due to Problems arise with AMR
spontaneous mutation within the bacterial chromosome or
by acquisition of entire resistance genes from other sources
AMR leads to the limitation of treatment options for
such as horizontal gene transfer which can occur through
infections and diseases caused by resistant bacteria
number of ways such as conjugation, transformation,
transduction etc. Plasmids are extra chromosomal genetic
-Extended period of treatment
elements which carry genes that encode for antimicrobial
-Usage of more than one drug to control the diseases
resistance. Some carry multiple resistance genes making
-Usage of second-line agents (modern and expensive
it possible for a bacteria to acquire multi drug resistance,
following a single gene transfer event.
-Not possible to treat with available drugs
Genetic alterations can result in resisting the action of t�
AMR which develops in zoonotic pathogen can enter
antibiotics by four different mechanisms identified;
human food chain.
decreased uptake of drugs, enzymatic inactivation or modification of the drug, structural modification of the t�
Most of the resistant determinants are located in
target molecule and production of an alternative target.
mobile genetic elements and they may use commensal bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Enterococci as
vehicles to transport in the population and transferred
to pathogenic organisms.
Altered target site
Livestock professionals are at risk of acquiring exposure to AMR bacteria from the animals they work with. Eg : spread of Multi-Resistance Staphylococcus aureus in livestock professionals.
The most common reason for drug resistance is inappropriate use of antimicrobials. In developing countries socio-economic and behavioural factors also contribute largely where anti microbial resistance surveillance programs are in rudimentary stage or not existing.
"Bypass" pathways
Pharmaceutical industry is reluctant to develop new antimicrobial drugs. Their painful experience is that the
Figure 01 : Four major biochemical mechanisms of costs of development are not recovered before the drugs antibiotic resistance.
are rendered inefficient.
Antimicrobial resistance in animal population has been How to overcome AMR
recorded in several occasions in the past; Penicillin in 1974;
Trertacycline in 1997; Avoparacin in 1999; Bacitracin, Use of responsible and prudent use of antimicrobials in
Spiromycine, Tylosin, Viginiamycine, in 2000. Strain of human and Veterinary medicine is a critical component.
Salmonella enteric Typhimurium DT204b was found Early and exact diagnosis of infection, using appropriate
resistant to nine microbial drugs causing clinical disease, drug at the correct dosage, and knowledge on resistance
traced to pre-shredded important lettuce: 2012. Denmark
of bacteria are important concepts to be kept in mind, in
surveillance study also reports that the monophasic
order to prevent AMR.
Salmonella Typhimurium isolates from pigs had high resistance to Ampicillin (65%), Streptomycine (67%) and Sulphonamide (67%), Tetracycline (65%).
Vet. Epid. Bulletin SL Vol. 06 No. 03
The OIE Global Conference on "Responsible and Prudent use of antimicrobs in animals" held in 2013 concluded with following recommendations,
quantities of antimicrobial agents used in food producing animals,
products in interaction with competent authorities and ensure efficient implementation.
�t� 4USFOHUIFO� � 7FUFSJOBSZ� 4UBUVUPSZ� #PEJFT� DBQBDJUZ� BOE� BVUIPSJUZ� UP� JOTUJUVUF� DPOUJOVJOH� QSPGFTTJPOBM� EFWFMPQNFOU�
and continuing education programs directed towards prudent use of antimicrobial agents and those that including diagnostic tests in animal health.
t�� 3FTFBSDI� � UP� JNQSPWF� UIF� VOEFSTUBOEJOH� PG� UIF� FċDBDZ� PG� DVSSFOU� BOUJNJDSPCJBM� BHFOUT� XIJMF� NJOJNJ[JOH� UIF�
development of resistance and find alternatives that could be used in animal production for antimicrobial agent substitutions.
combat animal diseases.
The World Animal Health Organization (OIE ) together with the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nation (FAO) work closely under the "Tripartite Alliance" to address the AMR as a major critical issue inaddtion to the control of zoonosis.
1. Danish Integrated Antimicrobial Resistant Monitoring and Research Program (DANMAP), 2012. National
Veterinary Institute, National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark.
2. World Animal Health Organization (OIE ) Antimicrobial Resistant Portal( AMR) IUUQ���XXX�PJF�JOU�GPS�UIF�NFEJB�BNS
2. Status of Livestock Diseases
2.1 Bovine Diseases
2.1.1 Bovine Babesiosis
A total of 800 cases of Bovine Babesiosis have been reported during the third
Spatial Distribution of
quarter of 2013. The pre-immunization program continued with immunizing
1000 calves in this period. The animals were immunized against B. bovis and B. bigemina strains .
Pre-immunization
July-Sept 2013
No. of Animals
Vet. Epid. Bulletin SL Vol. 06 No. 03
2.1.2 Bovine Brucellosis :
In the third Quarter 2013, there were 58 suspected
Bovine Brucellosis cases
cases of Bovine Brucellosis; recorded at Padiyatalawa,
Lankapura, Mannar, Musali, Vavuniya, Oddusuddan,
Balangoda, Ambalantota, Siyambalanduwa, Mahara, Eastern
Kalutara, and Marandagahamula Veterinary ranges. North Central
RBPT is carried out at Veterinary Investigation Northern
Center level as the screening test in suspected herds and as further confirmatory testing, CFT Sabaragamuwa
is carried out at Veterinary Research Institute. Southern
Vacnication programme is implemented through Uva
the respective Veterinary Investigation Centres at Western
locations identified to be at risk.
2.1.3. Black Quarter
A total of 19 Black Quarter cases were reported
Black Quarter Cases
with a Case Fatality Rate at 100%. The extensive
July- Sept 2013
outbreak was observed at Vavunia in which 15 cattle succumbed to death. Sporadic cases were
detected in 3 separate localities at Kurunegala,
Puttlam and Trincomalee. The Cattle Kurunegala
population at risk were vaccinated to contain the disease, resulting in vaccination of 33,699
cattle in Anuradhapura, Polonnaruwa, Puttlam,
Mannar, Mullaitivu, Vavuniya, Ampara, Total
Batticaloa, Trincomalee and Badulla districts.
2.1.4 Foot and Mouth Disease
Bovine Brucellosis cases
Foot and Mouth Disease was not reported
from any part of the country. Similarly there
were no cases reported in the same period of 2012.The only outbreak during this year was
detected at Uhana Veterinry range in Eastern
Province during the month of June. Prophylactic
vaccination program continued in the country
with 12,8921 number of cattle, buffalo and
goats being vaccinated during this period.
2.1.5 Mastitis :
In the third quarter, 2013 a total of 3303 clinical
Monthly distribution of cases of
cases of mastitis were reported. This is in
Mastitis :July-Sept 2013
comparison to the 2935 cases reported in the
same period in 2012. Locally prepared udder infusion lactating cow therapy, containing
Ampicillin and Cloxacllin are issued at field
level and it contributes to reduce te cost involved in treating mastitis cases in cows.
Vet. Epid. Bulletin SL Vol. 06 No. 03
2.2 Caprine Diseases
2.2.1 Contagious Pustular Dermatitis :
During the 3rd quarter of 2013, 441 cases
Distribution of CPD Cases
of Contagious Pustular Dermatitis has been
reported with death of 6 goats. More than 80% of the cases have been confined to three
provinces namely Northern, Eastern & North
Central with few cases in other provinces.The same period in year 2012 reported 208 cases and
9 deaths.An auto vaccine is locally produced at
District Veterinary Investigation Centre level, Total
based on the demand by relevant Veterinary Surgeon and also with the farmer cooperation.
2.3 Poultry Diseases
2.3.1 Fowl Pox :
Fowl Pox is reported from all over the island with a total of 9412 cases. Ampara, Jaffna, Batticaloa, Colombo districts reports higher incidences. Fowl pox is a disease that can be easily prevented by vaccination. However, vaccination coverage appears to be very low and clinical cases are found very often witnessing the endemic status in the country.
Occurrence of Fowl Pox
Vet. Epid. Bulletin SL Vol. 06 No. 03
2.3.2 Gumboro Disease :
Gumboro remains as the major poultry disease prevail in the country. Almost 8,000 birds succumbed to death during this three months period (July, Aug, Sept) due to this disease. In spite of large number of vaccines registered and used in the country, the disease is found in endemic status especially in poultry-belt area.
Distribution of Gumboro Cases : July-Sept 2013
2.3.3 Newcastle disease :
A total of 6830 cases of NCD was reported with a 1% CFR during the period under review. Mullaitivu, Jaffna and Kurunegala Districts report higher incidence of the disease. NCD Vaccine is locally produced at VRI. A total of 1,817,600 vaccine doses were issued to the field during this period. Apart from the hundred doses ampoules which are used free of charge in small scale operation, five hundred doses ampoules are also available at VRI for Rs. 100.00 to support the medium scale and large scale operation.
Occurrence of NCD : July-Sept 2013
2.3.4 Salmonellosis :
A total of 9097 Salmonellsis cases
Distribution of Salmonella Cases and
with a Case-Fatality Rate (CFR) at 2%
Deaths : July-Sept 2013
has been reported in the third quarter
2013. This is in comparison to the 9122
cases and a same CFR in the July-Sept 2012. Preventive vaccination against
Salmonellosis including Pulloram North Western
disease and Fowl typhoid is carried
out extensively in commercial poultry operation and also in limited number
of Poultry Breeder Farms.
Vet. Epid. Bulletin SL Vol. 06 No. 03
3. 1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Surveillance Program : July-Sept 2013
Commercial Poultry Serum
Pooled dropping and cloacal swabs
No. tested for AIV *
* Avian Influenza Virus
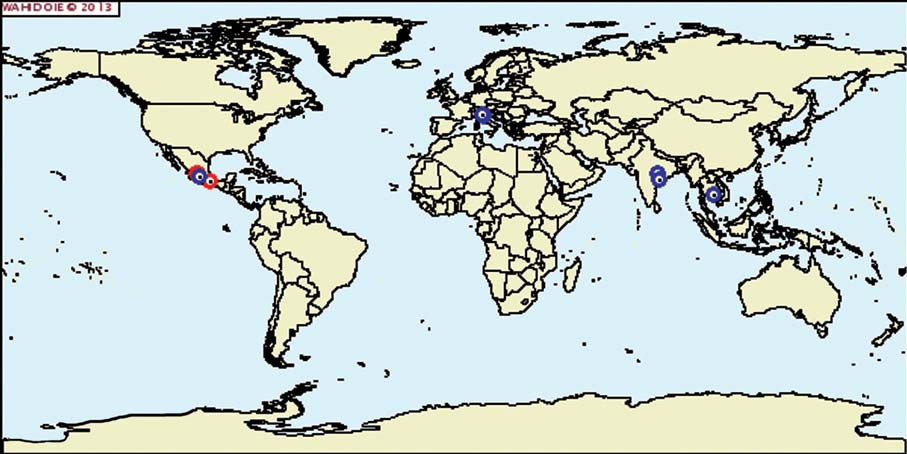
3.2 Global Distribution of Notifiable Avian Influenza: July-Sept 2013
Virus Type
Cambodia, Nepal, India
3.3 Global situation of HPAI outbreaks
Resolved (domestic)
Continuing - (domestic)
No - information
Vet. Epid. Bulletin SL Vol. 06 No. 03
Gastro Intestinal micro-organisms with different response to Antibiotics in animals and human
Compiled by:
Dr. (Mrs.) Ranjani Hettiarachchi
Division of Animal Health, Department of Animal Production & Health.
Dr. (Ms.) Bhagya Wickramasooriya
Tel : 081- 2388317
Mrs. Ranjani Weerasinghe
Editor:
Dr. Ranjani Hettiarachchi
Deputy Director Animal Health
Department of Animal Production & Health,
P.O. Box 13, Peradeniya.
E mail: [email protected]
PRINTED AT KANDY OFFSET PRINTERS (PVT) LTD TEL : 081 23 89 880
Source: http://www.daph.gov.lk/web/images/content_image/news_bulletins/epidemiological/veterinary_epidemiological_bulletin_volume_6_no_3.pdf
Beth Jacob's Vol. 26 - No. 2 february, march 2010 adar, NisaN 5770 Dates To Remember PURIM @BETH JACOB Saturday & Sunday, February 27 & 28 Special Purim Celebration for Young Children including Costume Parade & entertainment at 6:00 pm on Saturday, February 27. Mincha and Ma'ariv at 6:30 pm imme- diately followed by the reading
The Business Enablers Member of The Bank of East Asia Group About Tricor Business Services – Tricor Business Outsourcing Corporate Services – Tricor Evatthouse Investor Services – Tricor Barbinder Executive Resources – Tricor Executive Resources Tricor Group (Tricor), a member of The Bank of East Asia Group, is a global provider of integrated Business, Corporate and Investor Services. As a business enabler, Tricor provides outsourced expertise in corporate administration, compliance and business support functions that allows you to concentrate on what you do best - Building Business.





